Vicharak Linux Start Guide
Vicharak Provides multiple linux distributions for Vaaman SBC such as Debian, Ubuntu, Armbian, etc. This guide will help you to get started with Vicharak linux systems.
System Management
Set host name and password
Note
If you have installed Vicharak Debian or Ubuntu system from the official website, the default account name and password is:
username: vicharak
password: 12345
Vicharak Configuration Tool
Vicharak linux systems includes vicharak-config tool which is purely written using shell scripts that allows users to configure and setup their linux system configuration.
It provides a TUI interface to configure different linux specific configurations.
Use sudo vicharak-config to get started.
It is supported on all Debian based systems such as Debian buster/bullseye, Ubuntu focal/jammy and other third party systems such as Armbian.
Refer to
Vicharak config tool guide for more detailed information.
Set up automatic Wi-Fi connection on boot
In the following example, we will set up automatic Wi-Fi connection on boot for the wlan0 interface. This will be useful if you are using a headless system. That means you will not need to connect a monitor, keyboard, or mouse to your system to connect to Wi-Fi.
1. Edit the /userdata/before.txt file and add the following lines:
connect-wi-fi <network name> <password>
Example:
connect-wi-fi my-wifi-network my-wifi-password
2. Reboot the system.
Debugging
UART Serial Console
Windows users refer to
Getting Started with Vaaman UART Serial Console
Preparation
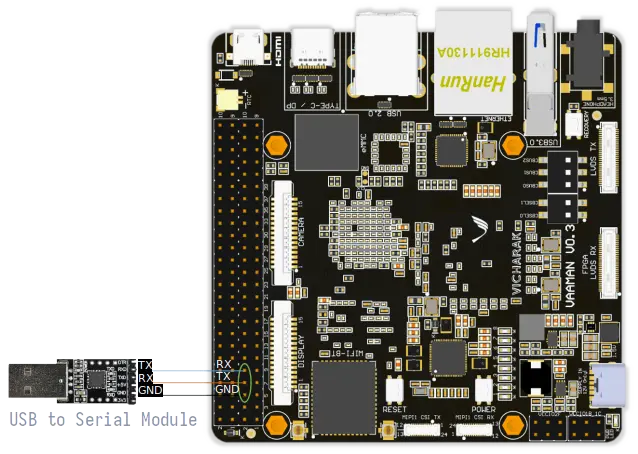
To access Vaaman SBC through the serial interface, A USB to TTL serial cable or adapter is required.
Hardware Setup
Connect the USB to TTL serial cable or adapter to your computer.
Connect the serial cable or adapter to the Vaaman SBC.
Serial FTDI Pin |
Header GPIO Pin |
Schematic Name |
|---|---|---|
GND |
Pin 6 |
GND |
TX |
Pin 8 (GPIO4_C4) |
UART2DBG_TX |
RX |
Pin 10 (GPIO4_C3) |
UART2DBG_RX |
Serial Console Programs
Install GTK-Term
You can install GTK-Term by executing the following command:
Debian/Ubuntu |
Fedora |
Arch Linux |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Setting up GTK-Term
Run GTK-Term by executing the following command:
sudo gtkterm
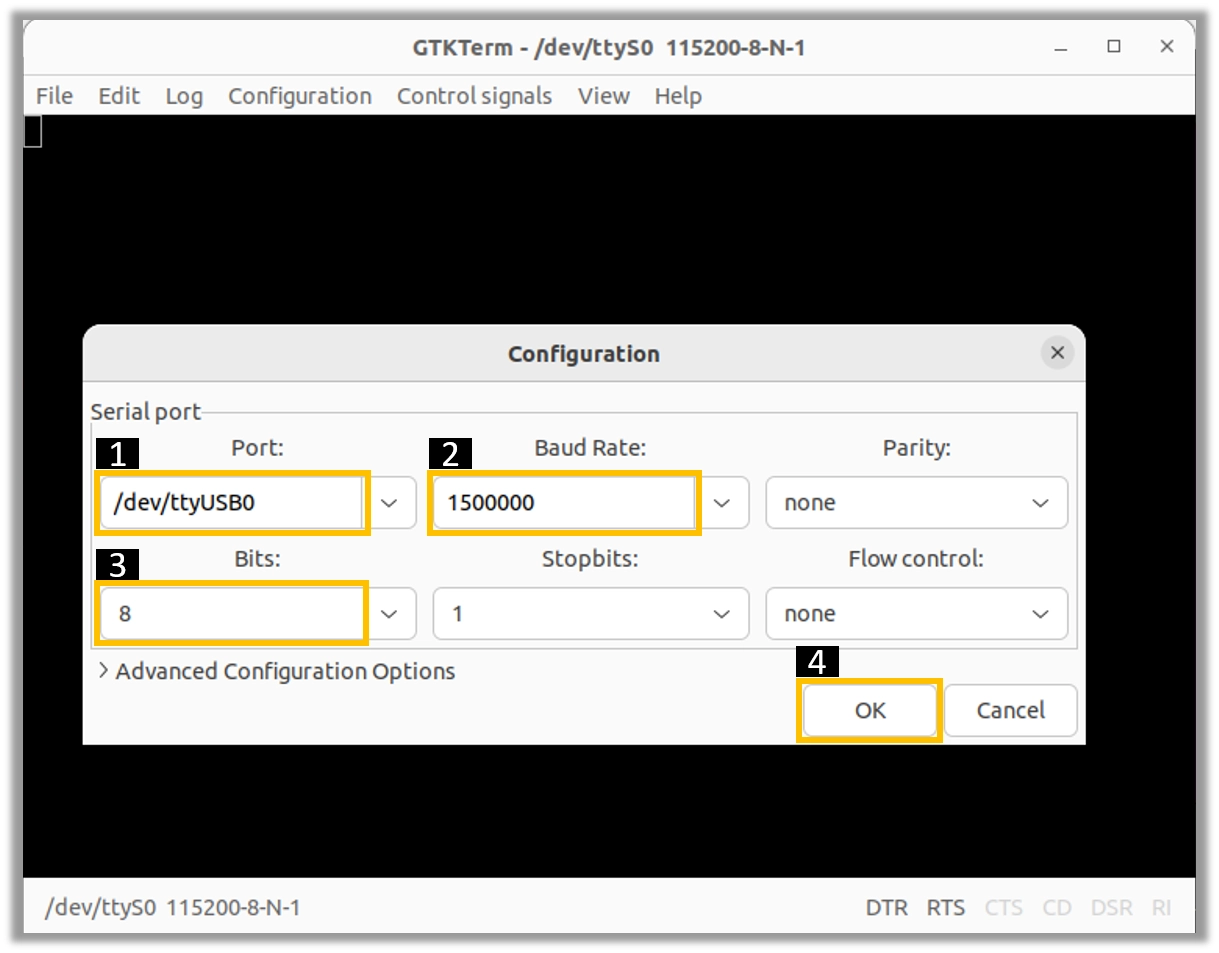
Configure GTK-Term
To access the configuration settings for GTK-Term, you can follow either of these methods:
Click on the Configuration menu and select Port.
OR
Press Ctrl+Shift+S.
By using either of these methods, you will be able to access the configuration settings in GTK-Term, where you can make adjustments to the port settings for your serial connection, as shown in the image below:
Note
Ensure that the cable is properly connected to the appropriate serial port on both devices.
Install Minicom
For Linux we will use Minicom. Install it with:
sudo apt install minicom
For other Linux distributions, please refer to the following table for the equivalent package names.
Debian/Ubuntu |
Fedora |
Arch Linux |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Setting up Minicom
Connect the USB to UART converter to your computer and run the following command to find the port name:
sudo minicom -s
Select Serial port setup and press Enter.
+-----[configuration]------+
| Filenames and paths |
| File transfer protocols |
| **Serial port setup** |
| Modem and dialing |
| Screen and keyboard |
| Save setup as dfl |
| Save setup as.. |
| Exit |
| Exit from Minicom |
+--------------------------+
Change the port name to the one you found in the previous step.
For example, if the port name is /dev/modem, then change it to /dev/ttyUSB0.
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| A - Serial Device : /dev/ttyUSB0 |
| B - Lockfile Location : /var/lock |
| C - Callin Program : |
| D - Callout Program : |
| E - Bps/Par/Bits : 115200 8N1 |
| F - Hardware Flow Control : Yes |
| G - Software Flow Control : No |
| |
| Change which setting? |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Screen and keyboard |
| Save setup as dfl |
| Save setup as.. |
| Exit |
| Exit from Minicom |
+--------------------------+
Configure baud rate of serial console according to your USB-UART converter.
Configure and Press Enter to save the settings.
+-----------------+---------[Comm Parameters]----------+----------------+
| A - Serial De| | |
| B - Lockfile Loc| Current: 1500000 8N1 | |
| C - Callin Pro| Speed Parity Data | |
| D - Callout Pro| A: <next> L: None S: 5 | |
| E - Bps/Par/B| B: <prev> M: Even T: 6 | |
| F - Hardware Flo| C: 9600 N: Odd U: 7 | |
| G - Software Flo| D: 38400 O: Mark V: 8 | |
| | E: 115200 P: Space | |
| Change which | | |
+-----------------| Stopbits |----------------+
| Screen a| W: 1 Q: 8-N-1 |
| Save set| X: 2 R: 7-E-1 |
| Save set| |
| Exit | |
| Exit fro| Choice, or <Enter> to exit? |
+---------+------------------------------------+
Select Save setup as dfl and press Enter.
+-----[configuration]------+
| Filenames and paths |
| File transfer protocols |
| Serial port setup |
| Modem and dialing |
| Screen and keyboard |
| **Save setup as dfl** |
| Save setup as.. |
| Exit |
| Exit from Minicom |
+--------------------------+
Save the settings as a different profile
If you want to save the settings as a different profile, select Save setup as.. and press Enter.
+-----[configuration]------+
| Filenames and paths |
| File transfer protocols |
| Serial port setup |
| Modem and dialing |
| Screen and keyboard |
| Save setup as dfl |
| **Save setup as..** |
| Exit |
| Exit from Minicom |
+--------------------------+
Select Exit and press Enter
+-----[configuration]------+
| Filenames and paths |
| File transfer protocols |
| Serial port setup |
| Modem and dialing |
| Screen and keyboard |
| Save setup as dfl |
| Save setup as.. |
| **Exit** |
| Exit from Minicom |
+--------------------------+
On successful configuration, you will see the following screen:
Welcome to minicom 2.8
OPTIONS: I18n
Compiled on Jan 9 2021, 12:42:45.
Port /dev/ttyUSB0, 16:33:28
Press CTRL-A Z for help on special keys
To exit Minicom, press Ctrl-A followed by X.
SSH Tutorial
Windows users refer to
Getting Started with Vaaman Using SSH
SSH Client installation
This guide will cover the installation of default openssh-server.
Debian/Ubuntu |
Fedora |
Arch Linux |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SSH Server installation
Debian/Ubuntu |
Fedora |
Arch Linux |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SSH Server Configuration
Enable SSH service to start on boot
sudo systemctl enable ssh
Start SSH service
sudo systemctl start ssh
Check SSH service status
sudo systemctl status ssh
Note
If it is active and running, you should see a active (running) message.
Check SSH service port
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep ssh
Avahi-daemon installation and configuration
You can install Avahi-daemon using the following commands:
Debian/Ubuntu |
Fedora |
Arch Linux |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
After the installation, Avahi-daemon should start automatically. If it does not, you can start it manually by running:
sudo systemctl start avahi-daemon
Verify its status by running:
sudo systemctl status avahi-daemon
Access Vaaman SBC through SSH
you can use either of the following commands:
SSH using the IP address
ssh username@ip_address
Tip
Replace “username” with the appropriate username for Vaaman and “ip_address” with the actual IP address assigned to Vaaman on the network.
SSH using the PC name (hostname)
ssh username@pc-name.local
Tip
Replace “username” with the appropriate username for Vaaman and “pc-name” with the actual PC name assigned to Vaaman on the network.